Sany Heavy Industry Sany Heavy Industry Co., Ltd. (SH:600031)
Trinity International Sany International (HK:00631)
Sany Renewable Energy Sany Renewable Energy (SH:688349)
Home > Industry information > Latest Practice! Key technology of deep shale gas horizontal well drilling in Sichuan Basin! The average depth of the hole is 5601m, the length of the horizontal section is 1884m, and the drilling cycle is shortened by 14.5%!
Latest Practice! Key technology of deep shale gas horizontal well drilling in Sichuan Basin! The average depth of the hole is 5601m, the length of the horizontal section is 1884m, and the drilling cycle is shortened by 14.5%!
2021.09.16
Oil and coal side
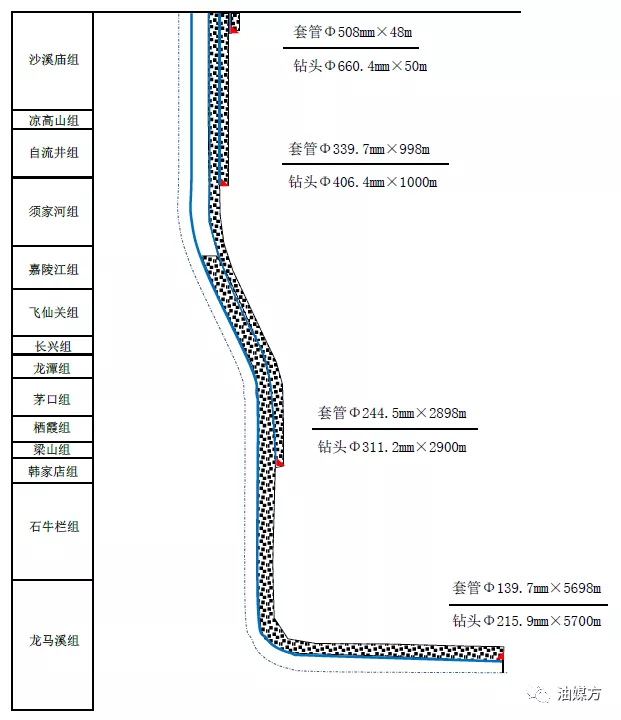 The Luzhou block is located in the low and steep structural belt in southern Sichuan, and the buried depth of the bottom boundary of the Longmaxi Formation is generally 3500.00~4500.00m, which gradually deepens from north to south. In 2019, the test gas production of Well Lu 203, with a vertical depth of 3890.00m, reached 1.38 million m³/d, which is the largest in China
The Luzhou block is located in the low and steep structural belt in southern Sichuan, and the buried depth of the bottom boundary of the Longmaxi Formation is generally 3500.00~4500.00m, which gradually deepens from north to south. In 2019, the test gas production of Well Lu 203, with a vertical depth of 3890.00m, reached 1.38 million m³/d, which is the largest in ChinaThe first test of a benchmark well for deep shale gas with a daily gas production of more than one million cubic meters. As the development of deep shale gas is in its infancy, the supporting technology of drilling and completion is in the exploration stage, and the drilling and completion technology of medium and deep shale gas such as Changning and Weiyuan is mainly used for reference. Fan Haofu et al. carried out the research on reducing the sliding footage of high slope screw drilling tools and reducing the density of drilling fluid by applying pressure-controlled drilling technology in the horizontal section, and Zang Yanbin et al. carried out the optimization of the well casing structure, and tested the speed-up tools such as hydraulic pressurizer and jet impactor, composite drill bit, pressure-controlled drilling and other technologies, and achieved good speed-up results.
However, there are still some difficulties in deep shale gas drilling in Luzhou, such as poor drillability of special lithologic formations, short rotary steering life affected by high formation temperature, and high difficulty in trajectory control due to the development of target stratum faults, resulting in low mechanical ROP, long drilling cycle, high accident complexity, and high drilling and completion costs. To this end, the wellbore structure and wellbore track were optimized, the wellbore trajectory control technology and high-performance oil-based drilling fluid were optimized, the drilling speed and efficiency improvement tools and technologies were promoted on a large scale, the pilot test of surface cooling equipment was carried out, and the key technology of drilling in Luzhou deep shale gas horizontal wells was popularized and applied, which greatly shortened the drilling cycle and achieved remarkable results.
Second, the key technology of drilling
1. Optimization of well structure
Considering the formation pressure, the point that must be sealed, the difficulty of drilling construction, the load of the drilling rig, the downhole risk, the economy and other factors, the wellbore structure of the deep shale gas horizontal well in Luzhou was optimized. On the premise of ensuring the realization of geological goals and safety, the casing layer, the length of the open hole section should be shortened as much as possible, and the frictional torque should be reduced, so as to provide a foundation for safe and efficient drilling and completion. The deep shale gas horizontal well in the Luzhou block adopts a pilot eye + triple wellbore structure, as shown in Figure 1. The φ508.00mm conduit generally goes down to the depth of about 50.00m, and the weathering leakage layer and collapse layer are sealed, and the well control can be appropriately deepened, while the φ339.70mm surface casing is generally lowered to the top of the Xujiahe Formation 10.00~30.00m, and the upper leakage layer, collapse layer and shallow gas are sealed, and the middle and lower part of the Xusi member can be deepened according to the needs of well control. φ244.50mm technical casing generally goes down to the top of Hanjiadian Formation about 30.00~50.00m, sealing the upper leakage, collapse, spray and other complex layers and sulfur-containing gas layers. φ139.70mm production casing to seal the target layer of Longmaxi.
2. Wellbore track optimization and control technology
The three-dimensional wellbore track used in the early stage is difficult to construct, the downhole risk is high, and the oblique torsion azimuth speed of the well enhancement is slow, which seriously affects the drilling cycle. Therefore, considering the factors such as cluster well collision prevention, friction torque, trajectory control difficulty, drilling speed, etc., the previous three-dimensional track design was optimized into a double two-dimensional borehole track, and the "straight-increase-steady-down-straight-increase-flatten" profile type was mostly adopted, with the control full-angle change rate of 1.00°~2.50°/30m in the upper well section, the full-angle change rate of the windowed well section was 4.00~6.00°/30m, and the control full-angle change rate in the horizontal section was not more than 3.00°/30.00m. Compared with the three-dimensional borehole track, the drilling torque of the "double two-dimensional" borehole track is reduced by 7.0%~14.0%, and the friction resistance is reduced by 11.5%~16.5%.
Taking into account safety, drilling speed and drilling cost, the horizontal section is divided into three stages, namely, the stage of drilling parameter release and acceleration, the stage of drilling acceleration and risk consideration, and the stage of risk reduction, as shown in Table 1. The stage of drilling parameter release and acceleration generally refers to the horizontal section with a length of less than 1000.00m, the drilling equipment capacity is sufficient, the downhole risk is low, the drilling speed is the mainstay, and the rotary guide is selected with large torque and long life straight screw to control the trajectory. The stage of drilling acceleration and risk balance generally refers to the well section with a horizontal section length of 1000.00~1500.00m, which reduces the capacity of drilling equipment and gradually increases the downhole risk, so it is necessary to take into account the drilling speed and downhole risk. If the downhole risk is small, the drilling speed is mainly increased, and the rotary guide is selected with large torque and long-life straight screw to control the trajectory. If the downhole risk is evaluated, the main focus is to reduce the drilling risk, and the rotary steering control trajectory is selected. The risk reduction stage generally refers to the well section with a horizontal section length of more than 1500.00m, in which the drilling equipment capacity basically reaches the limit and the downhole risk is high, so as to reduce the drilling risk. If the downhole risk is small, the rotary guide control trajectory is selected. If the downhole risk is evaluated, the near-drill gamma is selected with a 1.50° stabilizer-free bending screw and a hydraulic oscillator to control the trajectory.
3. Optimization of drilling speed tools and optimization of drill bits
(1) Drilling acceleration tools are preferred. The Xujiahe formation has high quartz content, small particle size and high hardness, and the average mechanical penetration rate is only 2.00~3.00m/h. The analysis shows that the reasons for the low drilling rate are: the conventional PDC bit is difficult to eat into the hard formation, the stick-slip effect is obvious, and the vibration of the drill bit and drill string is large, which is easy to cause the drill bit to collapse; The conventional PDC drill bit has poor aggressiveness and impact resistance, which cannot meet the demand for speed. To this end, the "3 blade PDC+3 cone wheel" composite drill bit is selected to cooperate with the hydraulic pressurizer, the cone wedge tooth of the composite drill bit improves the impact resistance of the drill bit, and the PDC knife wing with double row teeth improves the cutting efficiency and wear resistance. The hydraulic pressurizer absorbs the axial vibration of the drill string by hydraulic means to reduce the impact of the drill bit.
(2) Optimized design of PDC drill bit. The formation of Longtan Formation has high iron content and strong abrasiveness, and conventional PDC drill bits are easy to wear. The lithology of the Shiniulan Formation is dominated by dark gray limestone and argillaceous limestone, with high hardness, and it is difficult for conventional PDC drill bits to eat into the formation. Considering the characteristics of iron content and coal seam in Longtan Formation, a 6-wing double-row tooth PDC drill bit was designed, with a mixed distribution of φ16.00mm and φ13.00mm cutting teeth, and a tapered tooth for the rear row of teeth, so as to improve the aggressiveness of the drill bit and the ability to penetrate the interlayer. Focusing on the aggressiveness of the drill bit of the Shiniulan group, a 5-blade φ16.00mm cutting tooth PDC bit was designed, and the design of small camber angle was adopted to enhance the aggressiveness of the drill bit and improve the mechanical drilling rate.
3. Field test
The key technology was tested in 4 wells in Luzhou block, with an average depth of 5601.00m, a horizontal section length of 1884.00m, no downhole failure occurred during the drilling process, a mechanical ROP of 6.28m/h, and a drilling cycle of 110.06d, with good overall results, and a record of the longest (2550.00m) horizontal section of deep shale gas in China. Compared to wells without this technology, the ROP was increased by 5.5% and the drilling cycle was reduced by 14.5%. Taking Well B as an example, the application of this technology is described in detail.
Well B is designed to be drilled to a depth of 5383.00m, a vertical depth of 3610.21m, a predicted bottomhole temperature of 150.00°C, a three-open wellbore structure, a hydraulic pressurizer + composite drill bit, and an average mechanical ROP of 12.71m/h, which is 19.3% faster than that of adjacent wells. The OBM oil-based drilling fluid system is used in the horizontal section, the drilling fluid density is controlled at 2.10~2.20kg/L, the plastic viscosity is controlled at 75.00~80.00mPa.s, the demulsification voltage is controlled above 950.00V, the oil-water ratio is 88.00~95.00, and the filtration loss at high temperature and high pressure is 1.50~2.00mL, which meets the requirements of anti-collapse, lubrication and anti-jamming in the horizontal section and ensures the safe and efficient drilling of the horizontal section. The surface cooling system is used in the horizontal section from the depth of 4300.00m, the processing capacity is 1.20m³/min, and the bottom hole circulation temperature is reduced from 128.0°C to 124.0°C. When drilling to a depth of 5437.00m, the processing capacity is 1.80m³/min, and the bottom hole circulation temperature is reduced from 134.00°C to 129.00°C, which ensures the normal operation of the normal temperature rotary steering system. The 2612.00~5251.00m section of the well rotary directional drilling system and the long-life high-torque screw cooperate to control the wellbore trajectory, and the 5251.00~5437.00m section adopts the near-bit geosteering system, 1.50° angled screw drilling tools and hydraulic oscillators to control the wellbore trajectory, and successfully completes the horizontal section drilling, with a maximum full-angle change rate of 6.13°/30m, and a mechanical ROP of up to 6.95m/h in the horizontal section.
IV. Conclusions and Recommendations
(1) In view of the technical difficulties in the drilling of deep shale gas horizontal wells in the Sichuan Basin, the key technology of drilling deep shale gas horizontal wells was formed by optimizing the wellbore structure and borehole track, optimizing the wellbore trajectory control technology according to the downhole risk, optimizing the aggressive drilling parameters, optimizing the shock absorption and efficient rock breaking and speeding tools, and using the ground cooling equipment to ensure the normal operation of the rotary guide.
(2) The aggressive drilling parameters of "large drilling pressure, high rotation speed and large displacement" are conducive to improving the drilling speed and wellbore cleaning efficiency. Considering the acceleration effect, drilling tool safety and equipment capacity, the maximum drilling pressure of 150.00kN, the rotation speed of 120.00rpm and the displacement of 35.00L/s are recommended for horizontal drilling.
(3) Field tests show that the key technology of deep shale gas horizontal well drilling can solve the technical difficulties of deep shale gas horizontal well drilling in Luzhou block of Sichuan Basin.
(4) The surface cooling system of drilling fluid can basically meet the normal operation of the normal operation of the normal temperature rotary guide of the well section with the downhole circulating temperature less than 130.0°C, but with the increase of downhole temperature, the use of normal temperature rotary guide tools will be limited. It is suggested to speed up the introduction and R&D of high-temperature resistant rotary steering systems to meet the needs of safe and efficient development of deep shale gas.
0 comments
Related testimonials

CCTV Finance × Sany Heavy Industry: Infrastructure results are released! Anhui is soaring, and the equipment of the western port has become a "dark horse"
2025.05.19

China's installed wind and solar capacity has historically surpassed that of thermal power
2025.04.28

Breakthroughs have been made in the challenges of customization and high precision, and new progress has been made in the intelligent production of high-end equipment
2025.03.24






0 comments